In today’s digital landscape, businesses across Japan are embracing technologies that streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and deliver predictable outcomes. One such critical process is Application Lifecycle Management (ALM). With tools like Microsoft Power Apps, Power Automate, Power Pages, Microsoft Copilot Studio, and Dataverse, organizations in Japan can implement robust ALM strategies to meet the demands of a competitive market.
This blog explores the fundamentals of ALM, its key areas, and how businesses in Japan can leverage Microsoft Power Platform to achieve operational excellence.
What is Application Lifecycle Management?
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) refers to the end-to-end management of applications, encompassing governance, development, and maintenance. ALM integrates disciplines such as requirements management, software architecture, development, testing, deployment, and governance. It ensures predictable and repeatable software delivery by promoting collaboration between software development teams and related departments like testing and operations.
In Japan, where precision and efficiency are valued, ALM serves as a critical framework to enhance productivity, reduce errors, and deliver high-quality software solutions. By leveraging ALM tools, organizations can automate processes, streamline workflows, and ensure that teams work cohesively toward shared goals.
Core Disciplines of ALM:
Governance:
Includes requirements management, resource allocation, data security, user access control, change tracking, audits, and deployment management.
For Japanese companies adhering to strict compliance regulations, robust governance ensures transparency and accountability.
Application Development:
Encompasses problem identification, planning, designing, building, testing, and continuous improvement of applications.
Teams in Japan can integrate traditional developer roles with citizen developers for faster app development.
Maintenance:
Involves application deployment and the management of optional and dependent technologies.
Regular maintenance ensures applications remain secure and efficient, aligning with Japan’s focus on quality and reliability.
The ALM Lifecycle:
ALM is a cyclical process that includes:
Planning and tracking
Developing and building
Testing
Deploying
Operating
Monitoring
Learning from discovery
By following this iterative approach, organizations can continuously refine their applications and adapt to changing business needs.
ALM with Microsoft Power Platform: Unlocking New Possibilities in Japan
The Microsoft Power Platform provides a comprehensive ecosystem to implement ALM. It empowers organizations to securely store and manage data, automate processes, and drive collaboration—all while maintaining governance and compliance.
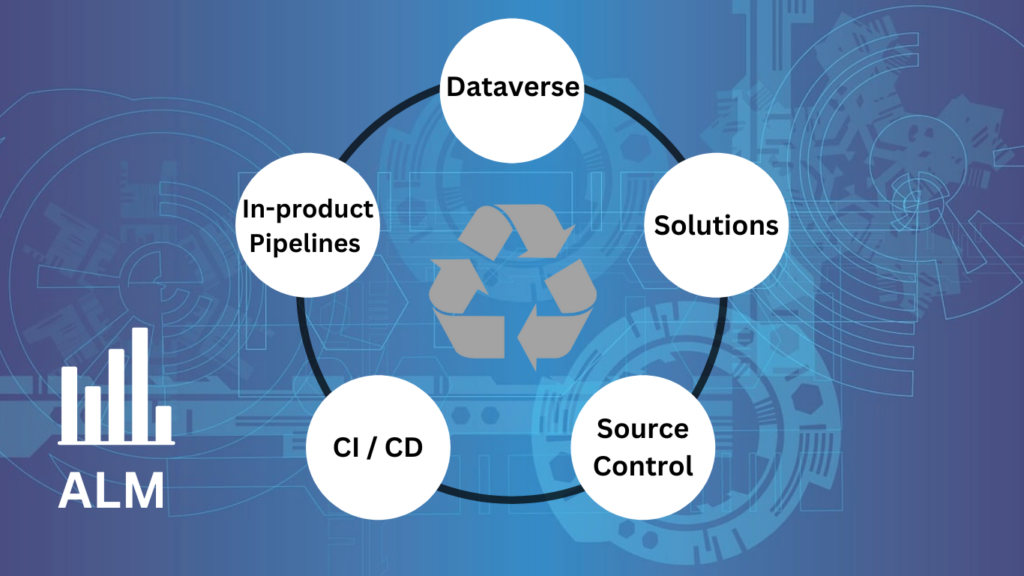
Key Components for ALM in Power Platform:
Dataverse:
Acts as a secure database for storing and managing business data and processes.
Japanese businesses can utilize Dataverse to maintain data integrity and enable seamless integration across environments.
Solutions:
Solutions are the backbone of ALM, enabling the distribution of components across environments via export and import.
Components can include tables, columns, apps, Power Automate flows, and plug-ins.
For companies in Japan, solutions provide a modular approach to building and deploying applications efficiently.
Source Control:
Serves as the single source of truth for storing and collaborating on components.
Teams can use tools like GitHub or Azure DevOps to maintain version control and ensure seamless collaboration.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD):
Platforms like Azure DevOps enable organizations to automate build, test, and deployment pipelines.
For Japanese enterprises, CI/CD ensures faster time-to-market and minimizes manual errors.
In-Product Pipelines:
Native deployment pipelines within the Power Platform simplify application delivery and reduce dependencies on external tools.
Why ALM Matters for Japanese Businesses
Japan’s unique business environment, characterized by rigorous quality standards and a focus on operational excellence, makes ALM an essential framework. By implementing ALM with the Power Platform, organizations can:
Enhance Efficiency: Automate repetitive tasks and improve resource allocation.
Ensure Compliance: Maintain data security and adhere to regulatory requirements.
Foster Collaboration: Unite cross-functional teams to work toward common objectives.
Drive Innovation: Accelerate application development and deployment to stay ahead of market demands.
Ready to Transform Your Application Lifecycle?
At Sysamic, we specialize in helping businesses in Japan leverage the full potential of the Microsoft Power Platform. With expertise in ALM, system development, and cloud solutions, we provide tailored strategies to meet your unique needs. Whether you’re just starting your ALM journey or looking to optimize your current processes, our team is here to guide you every step of the way.
Take the first step toward streamlined operations and predictable software delivery. Contact Sysamic today to learn how we can help your business achieve operational excellence with Microsoft Power Platform.
